Wrinkles and fine lines can be reduced with a common cosmetic procedure called Botox. Yet, Botox administration takes expertise and precision to guarantee safe and effective outcomes.
Know your facial structures

Having a solid understanding of facial anatomy before initiating Botox treatment is essential.
It’s crucial to have a firm grasp of facial anatomy before beginning Botox treatment. Knowing the area’s muscles, nerves, and blood vessels is essential. If you know how the body works, you can pinpoint the safest injection locations with ease. Knowing the patient’s medical history and the medications they are currently taking is also crucial to providing safe and effective care.
Reconstitute botox precisely
A safe and successful administration of Botox relies heavily on the medicine being properly reconstituted. To administer Botox, mix the powdered medication with a saline solution first. Use the recommended amount of saline solution that the manufacturer specifies when reconstituting to ensure good results. Both too much and too little saline can reduce the treatment’s efficacy. There is a window of time in which the reconstituted Botox must be utilized for maximum efficacy. A product should be utilized until it reaches its expiration date, after which it should be thrown away.
Be sure to inject properly
Administering Botox effectively and safely requires that the correct injection technique be used. The needle should enter the skin at a 90-degree angle and be pushed all the way in for the injection. The depth will change based on the area being treated and the patient’s skin thickness. Injecting too deeply raises the risk of problems and should be avoided. For the patient’s comfort and to ensure that the Botox is dispersed uniformly, the injection should be performed gently and gradually.
Learn your injection locations and dosage
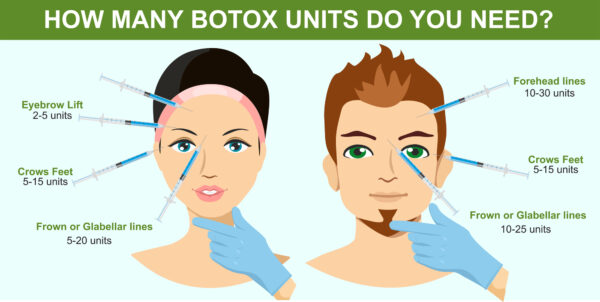
Botox dosage will be determined by factors such as the patient’s age, body mass index, and the severity of their wrinkles and muscle spasms.
One must be familiar with the recommended Botox dosage and injection sites before delivering the treatment. Individual differences in age, body mass index, and severity of wrinkles or muscle spasms will dictate dosing. When treating different areas, such as the forehead, crow’s feet, or neck, the injection locations will also change. If you want to administer Botox successfully, you need to have a firm grasp of facial and neck anatomy.
Keep tabs on patients and conduct regular checks
Monitoring the patient for unfavorable responses or side effects after Botox administration is essential. Examining the injection site for signs of inflammation, redness, or bruising is part of this process. The patient should be contacted after treatment is complete to gauge their level of satisfaction and address any remaining problems. Appointments for upkeep and dosing adjustments are essential for Botox to keep working as intended. Safe and effective Botox delivery, as well as a loyal patient following, can be achieved with careful patient monitoring and follow-up.
To ensure patient safety and the best possible treatment outcomes, only trained professionals should administer botox injections. Several fundamental approaches to remember when administering Botox are outlined below.
Consultation and Patient Evaluation:
- Learn everything you can about the patient’s current health situation, as well as their past treatments, drugs, and allergies.
- Choose the best injection locations and dosage by analyzing the patient’s facial anatomy, muscle strength, and skin condition.
- Talk to the patient about what they hope to achieve by receiving treatment and what they may experience as a result of it.
Reconstitution and storage procedures:
- Reconstitute the Botox powder according to the manufacturer’s instructions using a suitable diluent, typically sterile saline.
- Check the reconstituted Botox solution to make sure it is clear, colorless, and particle-free before applying it.
- To ensure the stability and efficacy of Botox, store the vials in a refrigerator at the recommended temperature.
Injection Technique:
- Find the exact muscles that cause the patient’s complaints, such as creases in the forehead, around the eyes, and the mouth.
- For accurate injections, a sterile needle with a tiny gauge should be used.
- Use the proper injection depth (intramuscular or subcutaneous) for the area being injected and the desired result.
- To avoid overdosing in one region, provide a series of tiny, evenly-spaced injections.
- To guarantee precise injection placement, you might think about using anatomical landmarks or grid patterns.
Medical personnel can learn the finer points of the Botox injection method through the training program Dentox. Get the knowledge required to comprehend cutting-edge techniques for improving the physical and mental health of your patients. To learn more about the online and live patient training sessions offered by Dentox, respectively, go to https://dentox.com/all-courses/botox-training and https://dentox.com/live-courses/.







